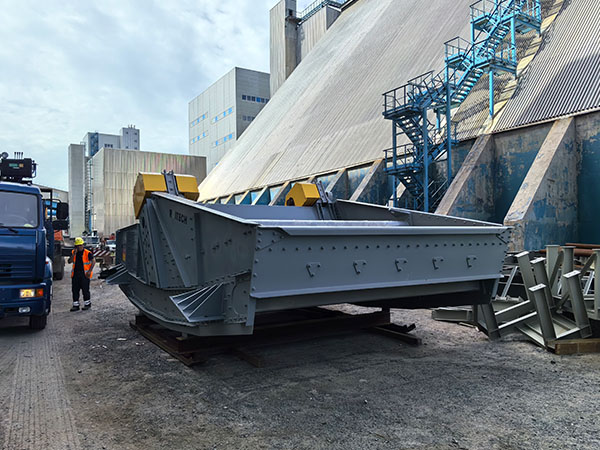
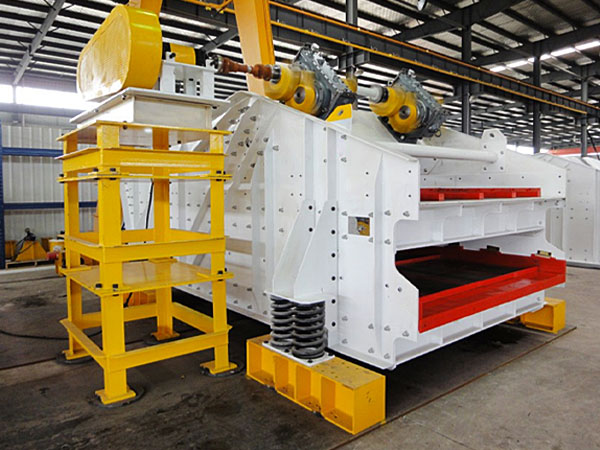
Cribas vibratorias Son equipos esenciales en diversas industrias., incluida la minería, construcción, procesamiento químico, y agricultura, para separar materiales basados en el tamaño. Sin embargo, inherentemente generan vibraciones y ruido importantes, que puede conducir a:
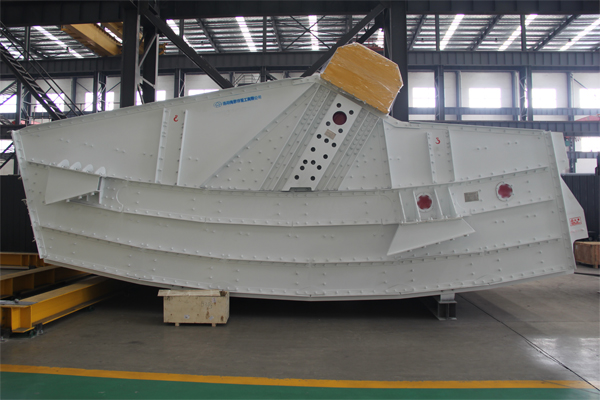

Fatiga estructural y falla de la pantalla y estructuras de soporte.
Reducción de la eficiencia de detección y precisión.
Operador Moltura y riesgos para la salud (pérdida auditiva, problemas musculoesqueléticos).
Contaminación ambiental (molestia).
Por lo tanto, La vibración efectiva y la reducción de ruido es crucial para mejorar el rendimiento, fiabilidad, y seguridad de las pantallas vibratorias. Esto implica un enfoque multifacético que abarca:
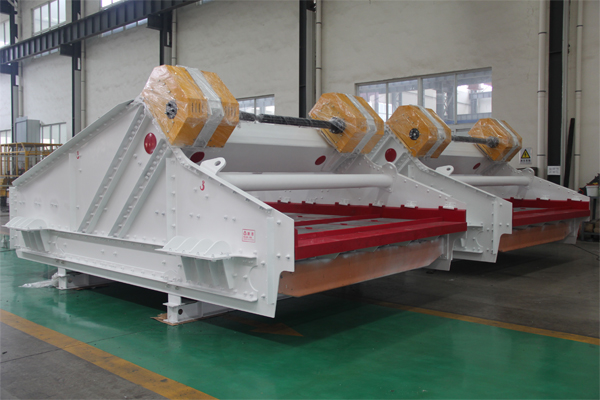

1. Vibratoria de optimización de la dinámica de la pantalla:
Comprender y optimizar el comportamiento dinámico de la pantalla vibratoria es el primer paso para minimizar la vibración y el ruido no deseados.. Esto incluye:
Análisis modal: Identificar las frecuencias naturales y las formas de modo de la estructura de la pantalla. Evitar la operación cerca de las frecuencias resonantes es crítico. Esto implica tanto el modelado teórico (Análisis de elementos finitos - FEA) y análisis modal experimental.
Análisis de fuerza: Determinar con precisión las fuerzas emocionantes generadas por el mecanismo vibratorio (p.ej., pesas excéntricas, vibradores electromagnéticos).
Análisis cinemático: Estudiar el movimiento de la cubierta de pantalla y el flujo de material para optimizar los parámetros de detección (amplitud, frecuencia, ángulo de carrera).
Equilibrio de masa: Equilibrar adecuadamente las masas giratorias u oscilantes para minimizar las fuerzas desequilibradas que contribuyen a la vibración. Esto incluye el equilibrio dinámico de los vibradores excéntricos.
Mojadura: Introducir la amortiguación para disipar la energía y reducir las amplitudes de vibración. Esto se puede lograr a través de:
Selección de materiales: Elegir materiales con propiedades de amortiguación inherentes.
Amortiguadores viscoelásticos: Aplicar materiales viscoelásticos a áreas críticas para absorber la energía de vibración.
Amortiguadores de fricción: Utilización de interfaces de fricción para disipar la energía a través del movimiento relativo.
Optimización de parámetros de excitación: Ajuste de la frecuencia, amplitud, y ángulo de carrera para minimizar la vibración mientras se mantiene una eficiencia de detección óptima.
Optimización estructural: Modificación de la estructura de la pantalla para aumentar la rigidez y alejar las frecuencias naturales de las frecuencias operativas. Esto podría implicar cambios en el grosor del material., nervaduras, o agregar soportes.
Optimización del flujo de material: Asegurar una distribución uniforme de material en la cubierta de la pantalla para evitar la carga desigual y los desequilibrios dinámicos.
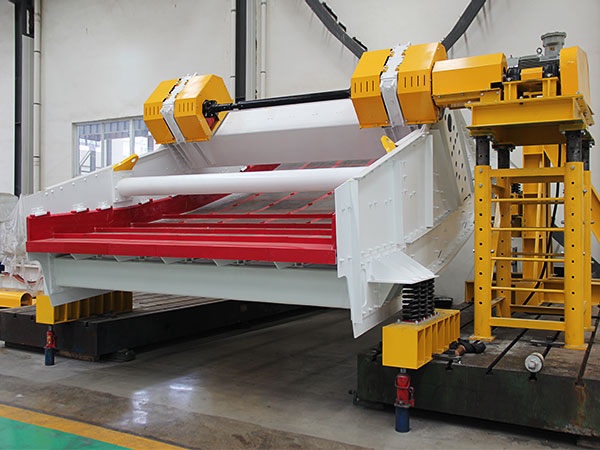

2. Aplicación de nuevas tecnologías de reducción de vibraciones:
Se pueden implementar varias tecnologías avanzadas para mitigar aún más la vibración y el ruido:
Control de vibración activo (AVC):
Utiliza sensores para detectar vibraciones y actuadores para generar fuerzas opuestas, cancelando efectivamente la vibración no deseada.
Complejo y costoso pero altamente efectivo para la reducción de vibración dirigida.
…
Para obtener información más detallada sobre la reducción de la vibración de la pantalla de vibración y la reducción de ruido, por favor haga clic aquí: https://www.hsd-industry.com/news/vibrating-screen-vibration-and-noise-reduction/