In today’s shipbuilding and marine engineering industry, the smallest components can have the biggest impact. Entre estos, pipe fittings play a critical role in ensuring the safety, la eficiencia, and longevity of marine vessels. Choosing the right material and working with a trusted manufacturer is not just a procurement decision—it’s a strategic investment in your vessel’s future.
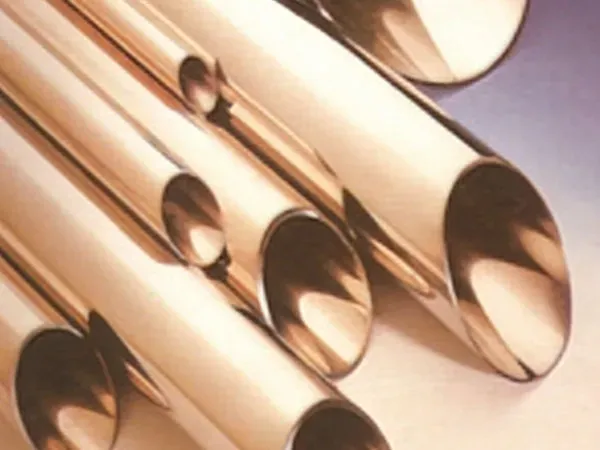
Copper-nickel alloys, known for their outstanding durability and corrosion resistance, have become the material of choice for pipelines exposed to seawater and other harsh marine environments. This article explores why custom copper-nickel ship pipe fittings are essential, the advantages of custom manufacturing, and how to select a reliable supplier to ensure long-term performance.
Why Copper-Nickel Is the Ideal Material for Marine Applications
Marine pipelines face challenges that ordinary materials cannot withstand. Saltwater, high pressures, fluctuating temperatures, and biofouling make corrosion and mechanical failure common concerns. Copper-nickel alloys, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% nickel, or variations optimized for specific projects, are engineered to meet these challenges:
Exceptional corrosion resistance: Copper-nickel alloys resist pitting and crevice corrosion, which are prevalent in seawater environments. Unlike standard stainless steel or carbon steel, these alloys maintain structural integrity over long periods, even in high-salinity conditions.
Reduced biofouling: The smooth surface of copper-nickel discourages marine growth such as barnacles and algae, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance.
Durable under extreme conditions: Copper-nickel fittings can handle high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, making them ideal for critical systems such as engine cooling lines, ballast water pipelines, and seawater circulation systems.
These properties make copper-nickel the preferred choice for pipelines carrying seawater, cooling water, and other fluids critical to ship operations. Vessels using these alloys experience fewer interruptions, lower maintenance costs, and longer service life.
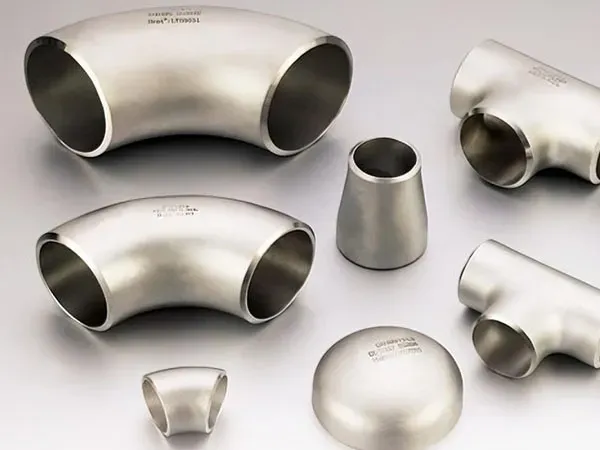

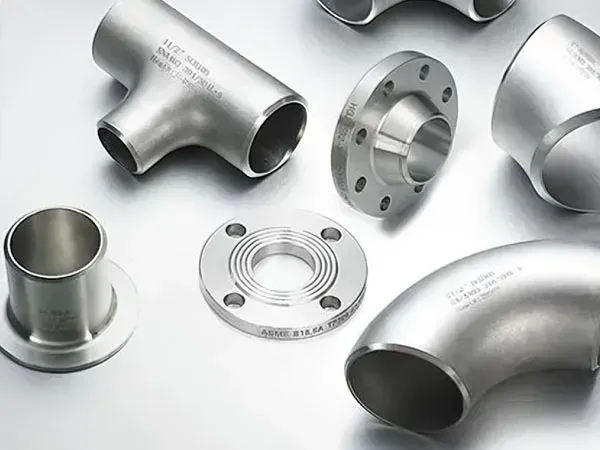
Advantages of Custom Copper-Nickel Fittings
While standard fittings are widely available, custom-manufactured solutions provide distinct benefits for modern marine projects:
1. Precision-Fit Designs
Every ship has unique specifications, and even minor deviations in pipe alignment can lead to leaks or operational inefficiencies. Custom fittings ensure exact dimensions that match your ship’s piping layout, reducing installation challenges and minimizing the risk of post-installation modifications.
…
For more detailed information on custom copper-nickel marine pipe fittings, por favor haga clic para visitar: https://www.zy-petrochemical.com/a/news/custom-copper-nickel-ship-pipe-fittings.html