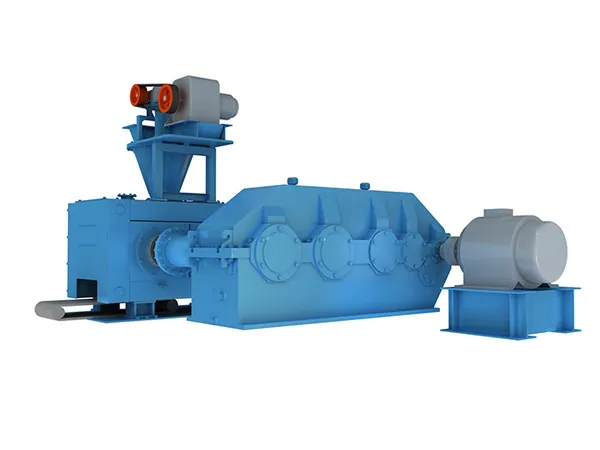
Gantry welding machines are specialized automated welding systems designed for high-precision, aplicaciones de soldadura a gran escala, particularmente en industrias como la construcción naval, fabricación de acero estructural, y fabricación de maquinaria pesada. Una máquina de soldadura de pórtico funciona según el principio de movimiento automatizado y control preciso del cabezal de soldadura sobre una pieza de trabajo..
Gantry welding machine working principle and how to achieve 0.1mm welding precision
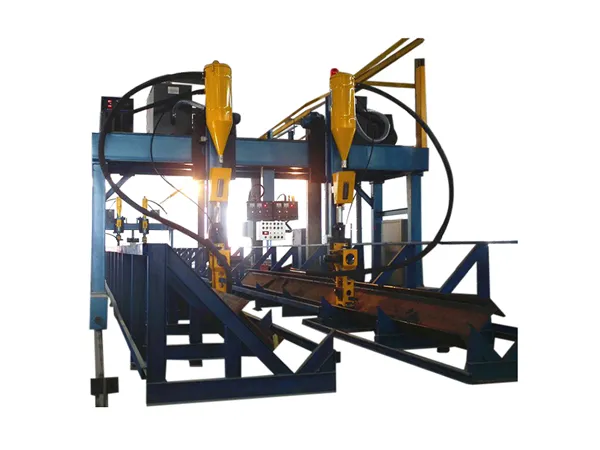

Gantry Welding Machines Working Principle
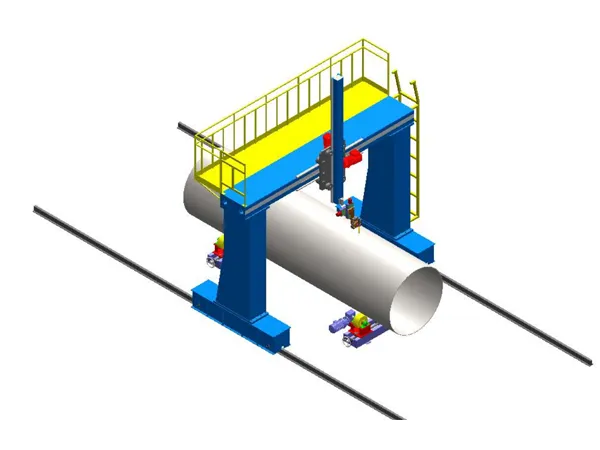
Estructura de pórtico: The machine features an overhead bridge-like structure (the gantry) that spans the welding area. This gantry provides a stable and rigid framework for the welding process.
Multi-Axis Movement: A carriage or trolley carrying the welding head moves along the gantry (typically the X-axis). The gantry itself can also move along rails (the Y-axis), and the welding head often has vertical movement (the Z-axis). This multi-axis movement allows the welding head to reach any point within the machine’s working envelope.
Automated Control System: The movement of the gantry and the welding head is controlled by a sophisticated numerical control (CNC) system or a programmable logic controller (PLC). This system directs servo motors that drive the movement along each axis with high precision.
Welding Process Integration: The gantry system is integrated with various welding power sources and equipment (p.ej., Soldadura de arco sumergido (SIERRA), Gas inerte metálico (A MÍ), Metal Active Gas (MAG)). The control system also manages the welding parameters such as voltage, actual, wire feed speed, and travel speed.
Seam Tracking (Optional but crucial for precision): Advanced gantry welding machines often incorporate seam tracking systems. These systems use sensors (p.ej., mecánica, láser, vision) to detect the actual weld joint in real-time and automatically adjust the welding head position to follow the seam accurately, even if the workpiece has slight variations or distortions.
Material Handling: While not directly part of the welding principle, gantry machines are often integrated with material handling systems (p.ej., transportadores, posicionadores) to move and orient the workpiece efficiently.
Achieving 0.1mm Welding Precision
Achieving such high welding precision (0.1mm) requires a combination of advanced technologies and meticulous engineering:
High-Precision Motion Control System:
High-Resolution Encoders: Servo motors on each axis must be equipped with high-resolution encoders to provide precise feedback on the welding head’s position.
This allows the control system to make minute adjustments to ensure accuracy.
…
More detailed information about the working principle of the gantry welding machine can be clicked to visit: https://www.bota-weld.com/en/a/news/gantry-welding-machine-working-principle.html