Improving the efficiency of tunnel lining construction is a multifaceted challenge that requires a holistic approach, from initial design to on-site execution. Key strategies focus on technological innovation, process optimization, and a highly coordinated workforce.
Cómo mejorar la eficiencia de la construcción del revestimiento de túneles

1. Optimize Design and Materials
Select the Right Lining Method: The choice between a precast segmental lining and a cast-in-place concrete lining is the most fundamental decision.
Precast Segments: Ideal for long, straight tunnels, especially in soft ground. Segments are manufactured off-site in a controlled environment, which ensures high quality and allows for simultaneous production and excavation, greatly speeding up the overall project.
Moldeado en el lugar (Titubear): Often more suitable for complex geometries, short tunnels, or areas where ground conditions make precast segments impractical. The use of advanced, fully automated tunnel lining trolleys can significantly increase the speed and precision of CIP construction.
Innovate with Concrete Mixes:
Fiber-Reinforced Concrete: Adding structural fibers (p.ej., steel or synthetic) can partially or completely replace traditional steel bar reinforcement. This reduces the time and labor required for rebar placement and can also improve the concrete’s tensile strength and durability.
High-Performance Concrete: Utilizing high-early-strength concrete with chemical admixtures can reduce the curing time required before formwork stripping and segment handling, accelerating the construction cycle.
Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC): This highly fluid concrete flows easily into the formwork, even around complex reinforcement, without the need for vibration. This saves time, reduces labor, and improves the final quality of the lining by eliminating honeycombing.
Implement Integrated Design: Design the tunnel and its lining from a “constructibilidad” perspectiva. This includes using numerical modeling and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to simulate construction stages, identify potential issues, and optimize the lining thickness and reinforcement to be both safe and efficient.
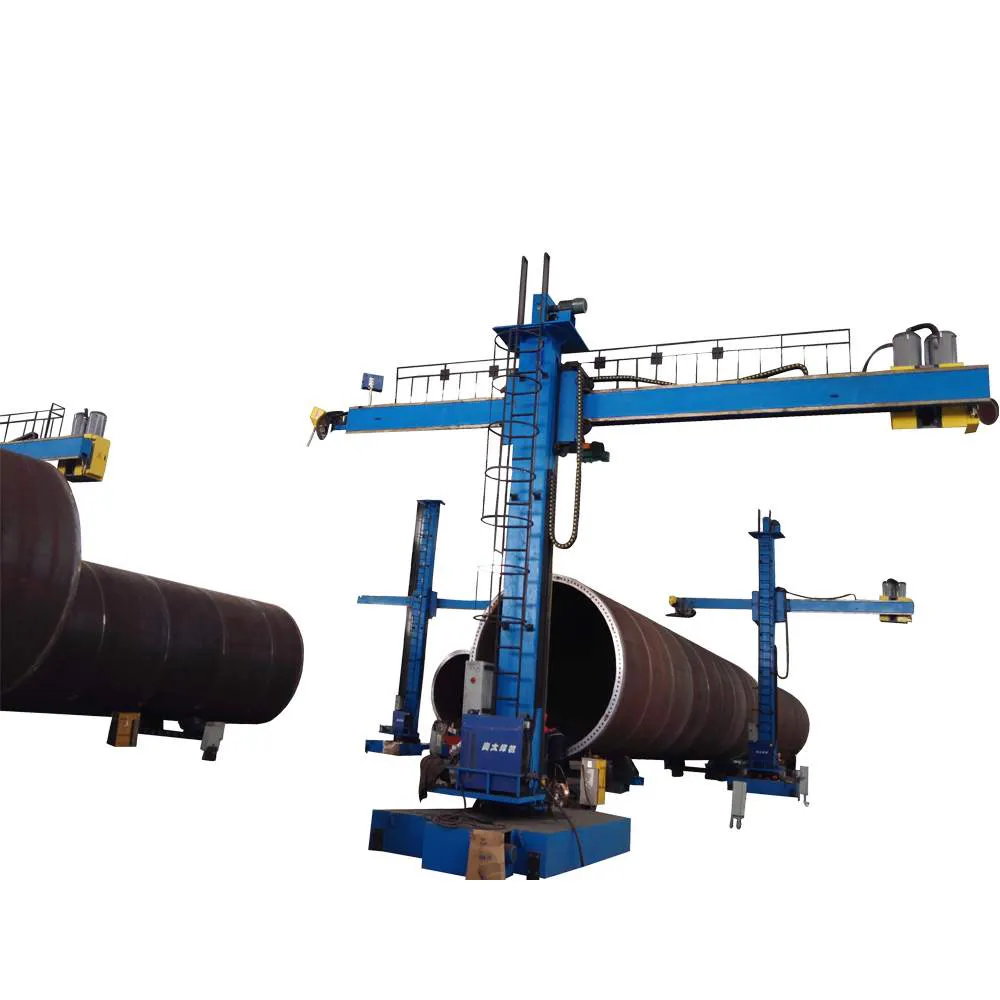
2. Leverage Advanced Machinery and Automation
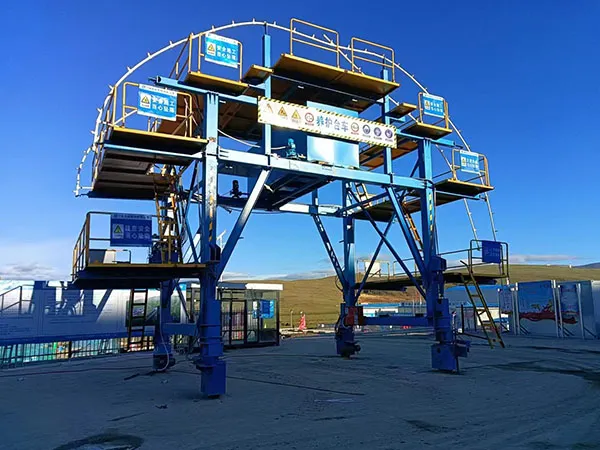
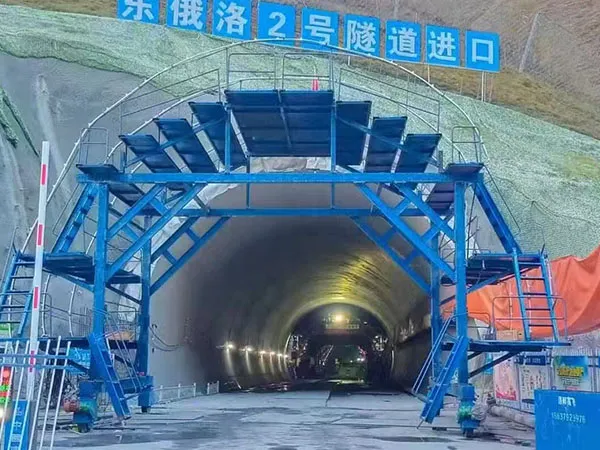
Utilize Fully Automated Formwork Systems: los carro de revestimiento de túneles is the heart of the operation.
Telescopic and Hydraulic Systems: Modern trolleys with telescopic formwork and hydraulic systems allow for rapid advancement and precise positioning. They can be operated by a small crew, reducing manual labor and the risk of error.
Integrated Functions: Look for trolleys that combine multiple functions, such as formwork stripping, Moviente, and re-erecting, into a single, automated cycle.
Adopt Smart Technologies and Robotics:
Automatización: Integrate automation for concrete pouring, vibración, and curing to ensure consistency and speed.
Real-time Monitoring: Use sensors and monitoring systems to track concrete strength, temperatura, and pressure. This data allows for real-time adjustments and ensures that the lining meets quality specifications, preventing costly rework.
robótica: Robotic systems can be used for repetitive or hazardous tasks like shotcrete application, surveying, or handling materials, which improves safety and consistency.
3. Streamline On-site Processes

Optimize Logistics and Supply Chain:
Entrega justo a tiempo: Coordinate with concrete suppliers and precast segment manufacturers to ensure materials are delivered precisely when needed. This minimizes on-site storage space and reduces potential material degradation.
…
More detailed information on how to improve tunnel lining construction efficiency can be found at: https://www.gf-bridge-tunnel.com/a/blog/improving-tunnel-lining-construction-efficiency.html