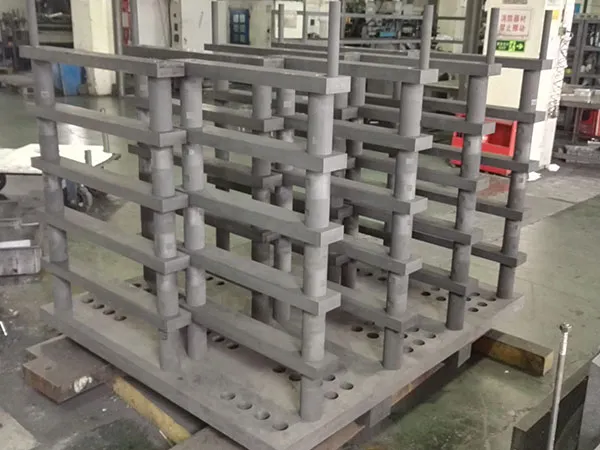
Настройка графитовой стойки для вакуумной печи является критическим процессом для оптимизации пропускной способности, обеспечение качества части, и максимизировать срок службы компонентов вашей печи. Хорошо спроектированный индивидуальный стеллаж может существенно улучшить вашу деятельность. графитовая стойка для вакуумной печи предполагает совместный процесс с производителем для проектирования и изготовления стойки, отвечающей вашим конкретным потребностям..
Зачем настраивать? Преимущества
Максимизируйте грузоподъемность: Установка большего количества деталей в каждом цикле, увеличение пропускной способности.
Улучшение качества деталей: Обеспечьте равномерный нагрев и поток газа вокруг каждой детали., уменьшение коробления и обеспечение стабильных металлургических свойств.
Предотвратить загрязнение: Надежно удерживайте детали без прямого контакта там, где это нежелательно., и используйте правильный сорт материала, чтобы предотвратить реакции.
Улучшите эргономику: Конструкция для легкой загрузки и разгрузки, снижение нагрузки на оператора и времени цикла.
Увеличение срока службы стойки: Используйте соответствующий материал и конструкцию конструкции, чтобы выдерживать термические циклы и механические нагрузки..
Процесс настройки графитовой стойки вакуумной печи
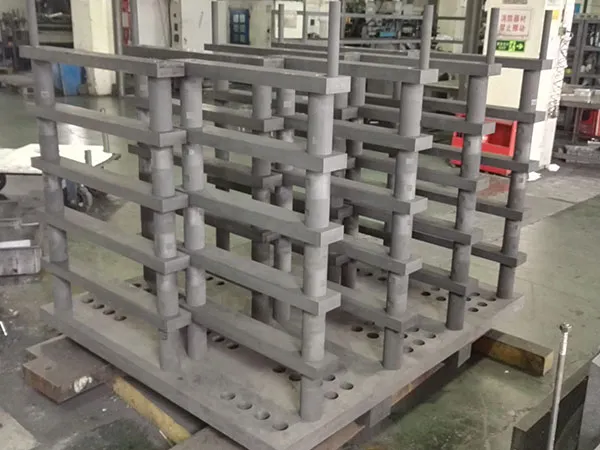

Обычно процесс следует следующим шагам::
Шаг 1: Определите свои требования
Оценка потребностей: Вы сообщаете производителю особенности вашего применения. Это включает в себя:
Геометрия и размер детали: Размеры и форма деталей, которые вы будете размещать в стойке..
Загрузка и вес: Общий вес деталей, которые должна выдержать стойка..
Рабочая температура: Максимальная температура, которой будет подвергаться стойка внутри печи..
Требуемая долговечность: Как долго вы ожидаете, что стойка прослужит и сколько термических циклов она должна выдержать?.
…
Для получения более подробной информации о том, как настроить графитовую стойку для вакуумной печи,, пожалуйста, нажмите здесь:https://www.czgraphite.com/a/news/customized-graphite-rack-for-vacuum-furnaces.html