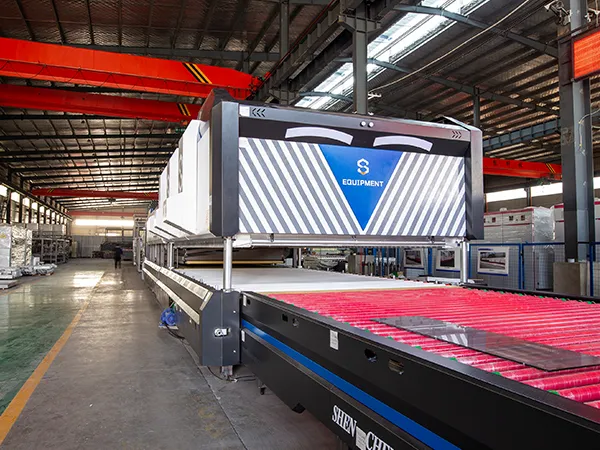
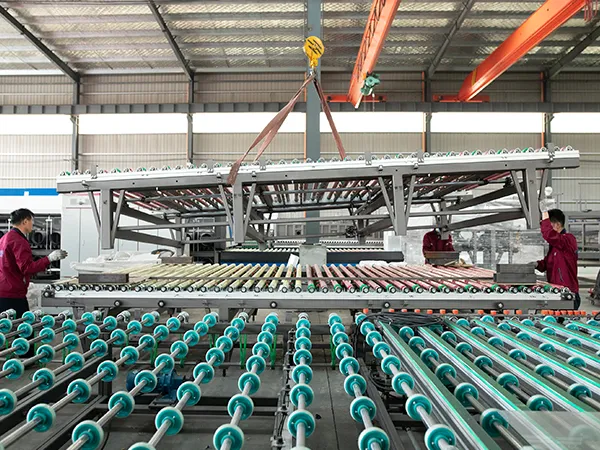
Alright, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of installing a glass tempering furnace. This is a complex piece of machinery, so a professional approach with meticulous attention to detail is crucial for safety and optimal performance.
Glass Tempering Furnace Installation
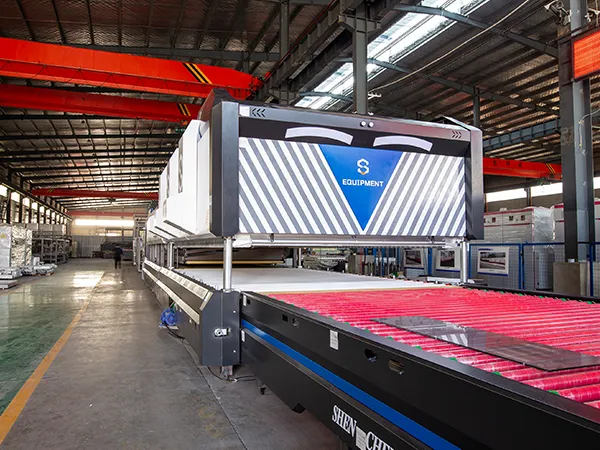

Phase 1: Pre-Installation and Site Preparation
Detailed Site Assessment:
A thorough inspection of the intended installation area is the first step. This involves verifying floor load capacity to support the furnace’s weight (which can be substantial).
Measurements of the space are taken to ensure adequate clearance around the furnace for operation, maintenance, and potential future removal or servicing.
Access routes for bringing in the large furnace components are carefully evaluated. This might involve planning for temporary removal of doors or even wall sections.
Utility Infrastructure Check and Preparation:
Electrical Power: The furnace’s power requirements (voltage, phase, current) are strictly adhered to. Dedicated electrical lines with appropriate circuit breakers and safety disconnects are installed by qualified electricians.
Gas Supply (if applicable): If the furnace uses gas for heating, the gas line capacity, pressure requirements, and safety shut-off valves are meticulously checked and installed according to local codes.
Compressed Air: Many tempering furnaces rely on compressed air for various functions, such as cooling and operating pneumatic cylinders. The existing compressed air system’s capacity and pressure are verified, or a dedicated compressor with appropriate piping is installed.
Water Supply (if applicable): Some advanced cooling systems might require a water supply. The water pressure, flow rate, and drainage system are assessed and prepared.
Ventilation System: Proper ventilation is critical to remove heat and any potential byproducts. The design and installation of the ventilation system must comply with environmental regulations and safety standards.
Foundation Preparation:
Depending on the furnace’s size and weight, a reinforced concrete foundation might be necessary to ensure stability and prevent settling. The foundation must be perfectly level.
Anchor bolts or embedded plates for securing the furnace frame are precisely positioned during the foundation pouring process.
Safety Perimeter and Access Control:
Before the furnace arrives, the installation area is clearly marked with safety barriers.
Access to the site is restricted to authorized personnel only.

Phase 2: Furnace Delivery and Positioning
Careful Unloading and Handling:
Specialized lifting equipment (cranes, forklifts with sufficient capacity) is used to unload the furnace components from the transport vehicles.
Rigging and lifting procedures are meticulously planned and executed by experienced personnel to prevent damage to the equipment and ensure the safety of the workers.
…
For more detailed information about glass tempering furnace installation, please click here: https://www.shencglass.com/en/a/news/glass-tempering-furnace-installation.html